Installing the Public Key. We need to install your public key on Sulaco, the remote computer, so that it knows that the public key belongs to you. We do this using the ssh-copy-id command. This command makes a connection to the remote computer like the regular ssh command, but instead of allowing you to log in, it transfers the public SSH key. Find out how to protect your server's sensitive data by learning how SSH keys work, creating an SSH key pair, and creating FTP users in SiteWorx. Dedicated Servers. Built-to-order dedicated infrastructure, customizable for your needs. Cloud Dedicated Servers. Set up SSH Keys Now that we got Git running, it is time to set up SSH keys for Git, so that we don’t need to input password every time. It is more convenient but also safer. The concept is we create a public/private key pair; put the public key to the remote server, and keep the private key on your local machine.
Setting up public-key SSH on Windows is much more tricky than on Linux (see here).
Install OpenSSH for Windows
In the following instructions, the example machine hostname (SSH server) is frak16, with username oqa in the domain OBJY.Sometimes, another machine (client) is used to connect to this frak16 machine to test connection settings.
(1) Install OpenSSH for Windows to the SSH server, e.g., frak16, at the following location SSH_DIR=C:spaceoqaOpenSSH.Use OpenSSH installer from here.Do NOT use OpenSSH for Windows from Sourceforge, which is outdated, even though many top links from Google search “OpenSSH windows” point to it.Select “Configure as Domain User” when installing.
(2) In the PATH environment variable, make sure that $(SSH_DIR)bin folder comes before MKS and Cygwin’s bins folder, if applicable.We need to use OpenSSH version of chmod and chown.
(3) Edit the file etc/passwd inside SSH_DIR (defined above).Make sure that the home directory for your username is present and in Cygwin notation, e.g., “/cygdrive/c/space/oqa” for user oqa.Make sure there is only one oqa user, like U-OBJYoqa (domain user) for OBJY domain.Delete other oqa users such as local users if needed.
(4) Edit $(SSH_DIR)etcbanner.txt to include welcome message that you prefer, to make it less verbose and more informative. I would change it to include the current host name to indicate which host is currently connected.
(5a) (Optional but recommended) Run SSH server is debug mode to verify that settings are correct. Run the following command for a test run:
(5b) Use ssh from another host (as client) to test connection. You will have to enter username and password to connect to frak16 from this client.
If the client is Windows and using OpenSSH, make sure the client’s etc/ssh_config file in its OpenSSH installation folder is as follows:
(6) After making sure the SSH is installed and working properly on frak16, run the following in a Command prompt with Admin power to start SSH as a service:
Now, you can connect to this Windows machine frak16 using password authentication.
Set up public-key SSH
(1) If the client is already set up, it should have its public key file. Copy content of that file to $(HOME_DIR).sshauthorized_keys file on the SSH server (e.g., frak16).
If you don’t have the public key file for the client, run ssh-keygen -t rsa on the client machine.The client machine’s public key file has the name like “id_rsa.pub”.
(2) On the SSH server (e.g., frak16), edit $(SSH_DIR)etcsshd_config to enable PubkeyAuthentication. The following lines must be enabled:
(3) Recursively from $(HOME_DIR), use chown to set ownership to oqa and chmod to set all folders and files in $(HOME_DIR).ssh to read-only.
(4) Run SSH server in debug mode again to verify that public-key SSH settings are correct.Run this command “ssh oqa@frak16 ‘ipconfig’” from the client machine and verify that no password is required.
Chrome app for mac download. (5) Start SSH server permanently by running, in an elevated Command Prompt.As of 2015 Feb, I tried running SSH as a Windows service but it does not work reliably.
Troubleshooting
Some of the most frequently encountered problems are discussed in this section.
Ownership of .ssh folder
You might encounter this problem when configuring public-key authentication.If you try to run the server in debug mode, you might see the following messages:
In this case, it’s an ownership problem on the SSH server.You can try another location for .ssh folder on the SSH server to see if it resolves the problem.In most cases, you can manually fix the above problem by using the following commands:
Note that chmod from OpenSSH must be used, instead of chmod from MKS or Cygwin.In addition, if there is a Local User oqa, remove that user so that chown will assign ownership to Domain User oqa.
Outdated SSH installer
If you see errors like this, you probably used OpenSSH installer from Sourceforge.That installer is outdated and buggy.Use the latest installer from here instead.
Cannot bind any address
You might find the following error message when connecting to an SSH server running in debug mode.
If you installed Cygwin and/or MKS on your Windows SSH server, their SSH services (sshd for Cygwin and secshd for MKS) are probably using the port 22.Verify that by using the following command in Windows:
You can turn off SSH services from Cygwin and MKS by going to Computer > Manage > Go to Services > Stop the relevant service (Windows 7).
File transfer
If you installed putty on Windows, note that you CANNOT simply use pscp (that is included with putty installation) to transfer file to another Windows machine with OpenSSH.
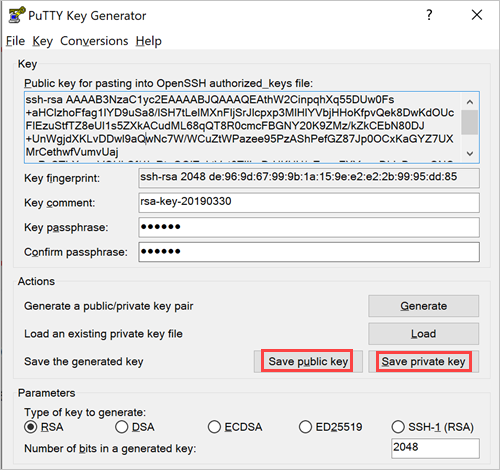
You have to convert the OpenSSH’s generated private key to a Putty private key, as detailed here.
An alternative is to use scp that is included with the OpenSSH installation. Note that this might not work (you still have to enter your password):
Since OpenSSH for Windows is extracted from Cygwin, trying Cygwin-style command turns out to be a good idea. This command allows password-less file transfer:
Note that files transferred over scp may not be readable (mode 000), regardless of file mode on the sending host.Therefore, remember to chmod a+r on the receiving host after file transfer, especially in an automation script, or you’ll get errors related to file access/file not found.
Other troubleshooting tips
- You may miss adding/setting some environment variables, e.g.,
PATH. After editing environment variables, you may need to restart your SSHD on a new Command Prompt windows to have those new environment variables in effect. - Remember to disable firewall on Windows machines.
Links
- And old tutorial: uses an old OpenSSH installer from Sourceforge. Most of the steps are not needed in the new installers.
This guide contains description of setting up public key authentication for use with WinSCP. You may want to learn more about public key authentication or SSH keys instead.
- Configure Server to Accept Public Key
Advertisement
Before starting you should:
- Have WinSCP installed;
- Know how to connect to the server without public key authentication.
If you do not have a key pair yet, start with generating new key pair.
Connect to your SSH server using WinSCP with the SSH protocol, using other means of authentication than public key, e.g. typically using password authentication.
Once logged in, configure your server to accept your public key. That varies with SSH server software being used. The most common SSH server is OpenSSH.
You can use Session > Install Public Key into Server command on the main window, or Tools > Install Public Key into Server command on SSH > Authentication page page on Advanced Site Settings dialog. The functionality of the command is similar to that of OpenSSH ssh-copy-id command.
Ssh Public Key Windows
Or you can configure the key manually:
- Navigate into a
.sshsubdirectory of your account home directory. You may need to enable showing hidden files to see the directory. If the directory does not exists, you need to create it first. - Once there, open a file
authorized_keysfor editing. Again you may have to create this file, if this is your first key. - Switch to the PuTTYgen window, select all of the text in the Public key for pasting into OpenSSH authorized_keys file box, and copy it to the clipboard (
Ctrl+C). Then, switch back to the editor and insert the data into the open file, making sure it ends up all on one line. Save the file. WinSCP can show you the public key too. - Ensure that your account home directory, your
.sshdirectory and fileauthorized_keysare not group-writable or world-writable. Recommended permissions for.sshdirectory are700. Recommended permissions forauthorized_keysfiles are600. Read more about changing permissions.
There are some specifics when setting up the public key authentication on OpenSSH server on Windows.
- Save a public key file from PuTTYgen, and copy that into the
.ssh2subdirectory of your account home directory. - In the same subdirectory, edit (or create) a file called
authorization. In this file you should put a line likeKey mykey.pub, withmykey.pubreplaced by the name of your key file.
For other SSH server software, you should refer to the manual for that server.
When configuring session, specify path to your private key on SSH > Authentication page of Advanced Site Settings dialog.
Alternatively, load the private key into Pageant.
Cloud providers have typically their own mechanism to setup a public key authentication to virtual servers running in the cloud.
For details see guides for connecting to:
Ssh Add Public Key
- Amazon EC2;
- Google Compute Engine;
- Microsoft Azure.
Ssh Using Public Key
- Using public keys for authentication;
- Using PuTTYgen;
- Understanding SSH key pairs.
