- The Azure CLI is available across Azure services and is designed to get you working quickly with Azure, with an emphasis on automation. Key Characteristics Azure CLI capabilities make it easy to work with different programing languages and software environments. For example, Azure CLI: Is available to install in Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Azure Bot Services Intelligent, serverless bot services that scale on demand Machine Learning Build, train, and deploy models from the cloud to the edge Azure Databricks Fast, easy, and collaborative Apache Spark-based analytics platform.
- You can use Azure AD Domain Services (Azure AD DS) in your Remote Desktop Services deployment in the place of Windows Server Active Directory. Azure AD DS lets you use your existing Azure AD identities in with classic Windows workloads. With Azure AD DS you can: Create an Azure environment with a local domain for born-in-the-cloud organizations.
- You can use Azure AD Domain Services (Azure AD DS) in your Remote Desktop Services deployment in the place of Windows Server Active Directory. Azure AD DS lets you use your existing Azure AD identities in with classic Windows workloads. With Azure AD DS you can: Create an Azure environment with a local domain for born-in-the-cloud organizations.
 -->
-->You can use Azure AD Domain Services (Azure AD DS) in your Remote Desktop Services deployment in the place of Windows Server Active Directory. Azure AD DS lets you use your existing Azure AD identities in with classic Windows workloads.
Use the Windows Authentication section of the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server to enable and configure Windows authentication for applications. Before you set up Windows Authentication, keep the following list in mind: After setup, reboot the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication for.
With Azure AD DS you can:
- Create an Azure environment with a local domain for born-in-the-cloud organizations.
- Create an isolated Azure environment with the same identities used for your on-premises and online environment, without needing to create a site-to-site VPN or ExpressRoute.
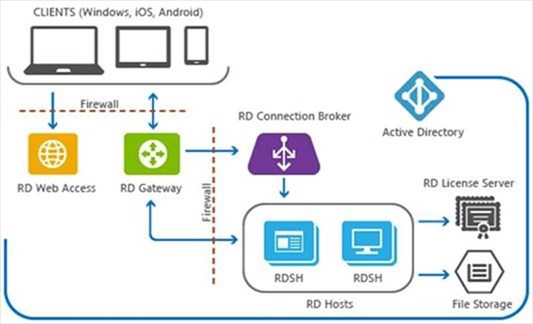
When you finish integrating Azure AD DS into your Remote Desktop deployment, your architecture will look something like this:
To see how this architecture compares with other RDS deployment scenarios, check out Remote Desktop Services architectures.
To get a better understanding of Azure AD DS, check out the Azure AD DS overview and How to decide if Azure AD DS is right for your use-case.
Use the following information to deploy Azure AD DS with RDS.
Prerequisites
Before you can bring your identities from Azure AD to use in an RDS deployment, configure Azure AD to save the hashed passwords for your users' identities. Born-in-the-cloud organizations don't need to make any additional changes in their directory; however, on-premises organizations need to allow password hashes to be synchronized and stored in Azure AD, which may not be permissible to some organizations. Users will have to reset their passwords after making this configuration change.
Deploy Azure AD DS and RDS
Use the following steps to deploy Azure AD DS and RDS.
Enable Azure AD DS. Note that the linked article does the following:
- Walk through creating the appropriate Azure AD groups for domain administration.
- Highlight when you might have to force users to change their password so their accounts can work with Azure AD DS.
Set up RDS. You can either use an Azure template or deploy RDS manually.
Use the Existing AD template. Make sure to customize the following:
Settings
Resource group: Use the resource group where you want to create the RDS resources.
Note
Right now this has to be the same resource group where the Azure resource manager virtual network exists.
Dns Label Prefix: Enter the URL that you want users to use to access RD Web.
Ad Domain Name: Enter the full name of your Azure AD instance, for example, 'contoso.onmicrosoft.com' or 'contoso.com'.
Ad Vnet Name and Ad Subnet Name: Enter the same values that you used when you created the Azure resource manager virtual network. This is the subnet to which the RDS resources will connect.
Admin Username and Admin Password: Enter the credentials for an admin user that's a member of the AAD DC Administrators group in Azure AD.
Template
Remove all properties of dnsServers: after selecting Edit template from the Azure quickstart template page, search for 'dnsServers' and remove the property.
For example, before removing the dnsServers property:
And here's the same file after removing the property:
Deploy RDS manually.
Use the Windows Authentication section of the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server to enable and configure Windows authentication for applications. Before you set up Windows Authentication, keep the following list in mind:
- After setup, reboot the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication for Terminal Services to take effect.
- If 'Require Azure Multi-Factor Authentication user match' is checked and you are not in the user list, you will not be able to log into the machine after reboot.
- Trusted IPs is dependent on whether the application can provide the client IP with the authentication. Currently only Terminal Services is supported.
Important
As of July 1, 2019, Microsoft no longer offers MFA Server for new deployments. New customers that want to require multi-factor authentication (MFA) during sign-in events should use cloud-based Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
To get started with cloud-based MFA, see Tutorial: Secure user sign-in events with Azure AD Multi-Factor Authentication.
Existing customers that activated MFA Server before July 1, 2019 can download the latest version, future updates, and generate activation credentials as usual.
Note
Terminal Server In Azure
This feature is not supported to secure Terminal Services on Windows Server 2012 R2.
To secure an application with Windows Authentication, use the following procedure
- In the Azure Multi-Factor Authentication Server click the Windows Authentication icon.
- Check the Enable Windows Authentication checkbox. By default, this box is unchecked.
- The Applications tab allows the administrator to configure one or more applications for Windows Authentication.
- Select a server or application – specify whether the server/application is enabled. Click OK.
- Click Add…
- The Trusted IPs tab allows you to skip Azure Multi-Factor Authentication for Windows sessions originating from specific IPs. For example, if employees use the application from the office and from home, you may decide you don't want their phones ringing for Azure Multi-Factor Authentication while at the office. For this, you would specify the office subnet as Trusted IPs entry.
- Click Add…
- Select Single IP if you would like to skip a single IP address.
- Select IP Range if you would like to skip an entire IP range. Example 10.63.193.1-10.63.193.100.
- Select Subnet if you would like to specify a range of IPs using subnet notation. Enter the subnet's starting IP and pick the appropriate netmask from the drop-down list.
- Click OK.
Azure Mfa Terminal Services
Next steps
